Subproject C7
Simulation of adhesives curing and shrinking processes within piezo-metal-composites
Project Manager:
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Jörn IhlemannTechnische Universität Chemnitz
Fakultät für Maschinenbau
Institut für Mechanik und Thermodynamik
09107 Chemnitz
Telephon: +49-(0)371 / 531 36946
Telefax: +49-(0)371 / 531 23419
E-Mail: joern.ihlemann@mb.tu-chemnitz.de
Motivation
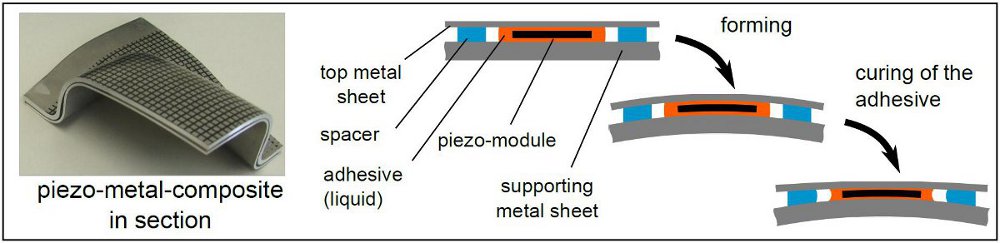
Since piezo-elements sustain only very small deformations without being damaged, the large deformations due to the forming process must be kept off these elements. For this reason the elements get embedded in an adhesive between a supporting bottom metal sheet and an additional top metal sheet. The production process is designed in such a way that the curing of the adhesive occurs after the forming (cf. Figure ) . Thus, the adhesive works as a floating support for the deformation-sensitive piezo-elements. Consequently, this requires relatively thick adhesive layers. Therefore, shrinkage processes during the curing and cooling of the adhesive remarkably gain in importance.
Proceeding
The scientific approach in designing the virtual simulation contains the following steps:| - | Development of a material model that is able to represent the thermomechanical-chemical coupled curing processes in the adhesive. |
| - | Implementation of the material model in a scientific software for the fast solution of homogeneous deformations and furthermore in the user subroutine USERMAT of the commercial Finite-Element-System ANSYS for the simulation of 3-dimensional heterogeneous deformations. |
| - | Development of a problem-specific software for the identification of parameters of this material model. This software has to account for the specific effects that come along with the phase transition of the adhesive from a liquid to a solid phase and the cooling of the material respectively. |
With the prediction of these three basic effects the main objective of the application to defined composite-layouts is achieved: the evaluation and the comparison of different adaptronic piezo-metal composite layouts with respect to the impact of the curing and shrinkage processes after the forming.




